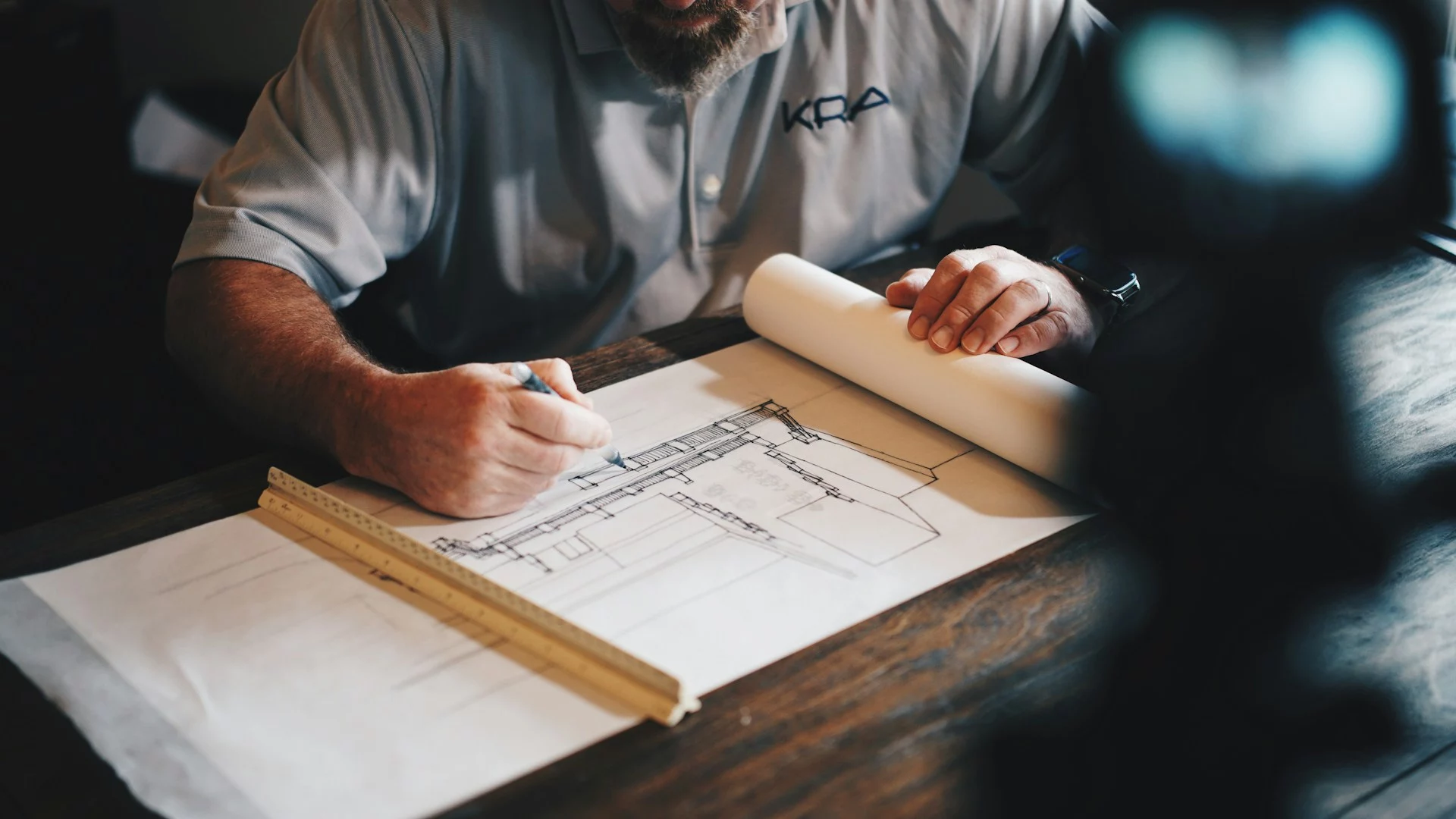
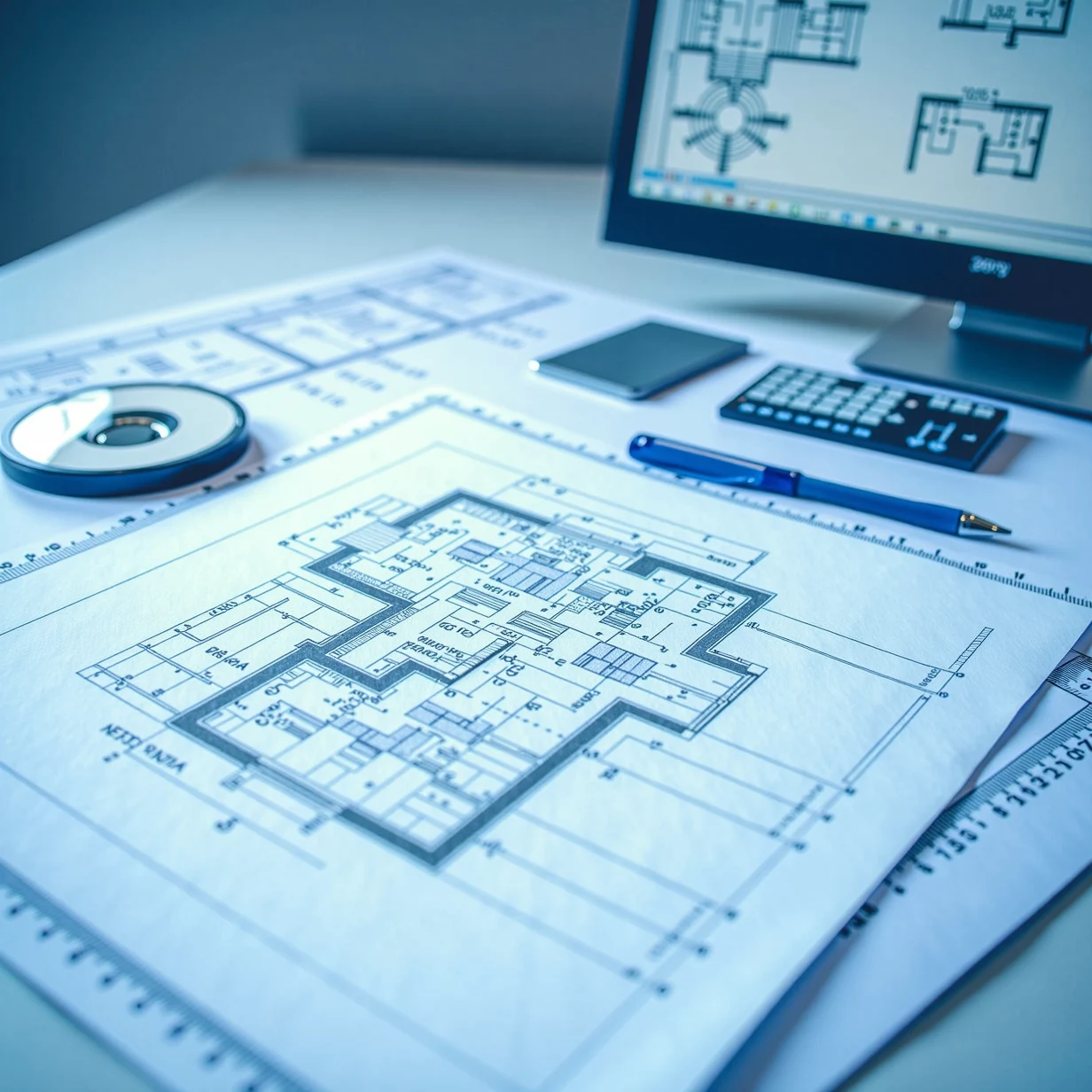
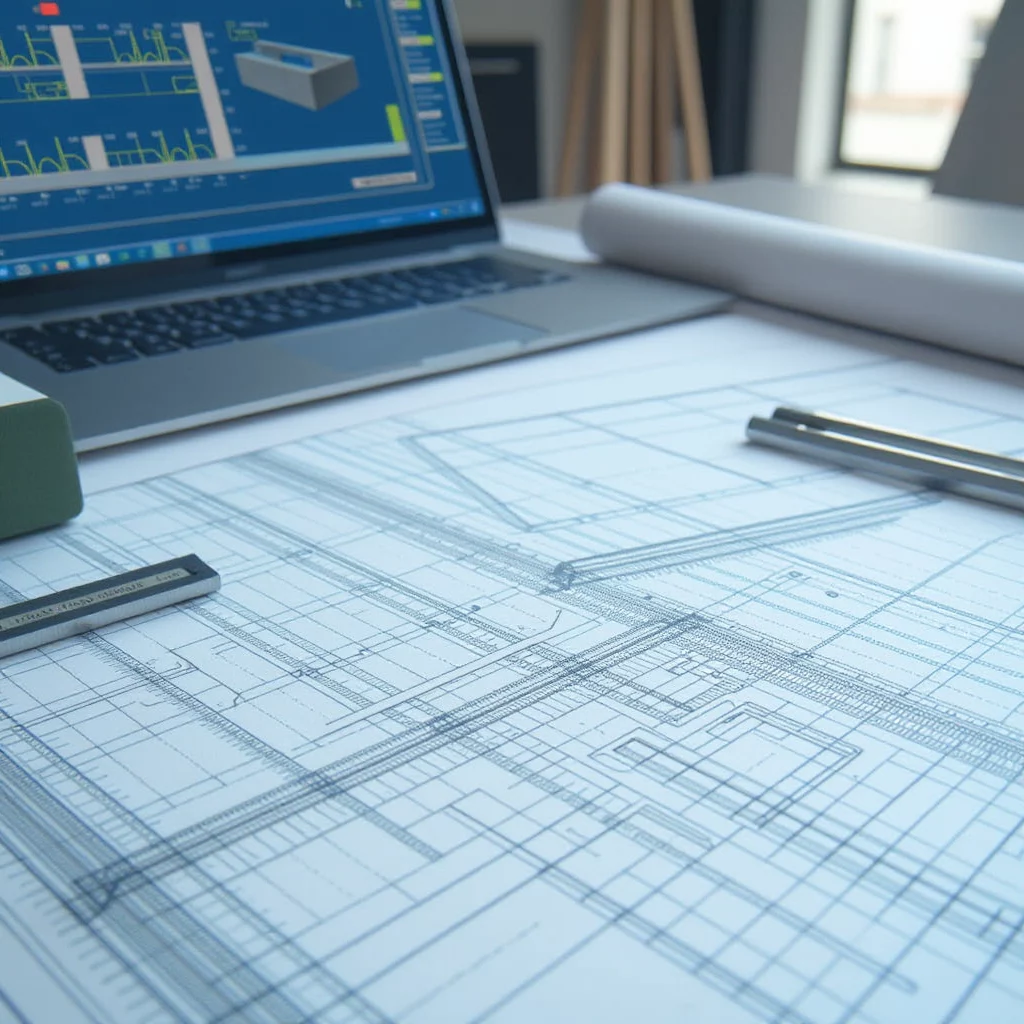
Understanding Structural 2D Drafting: Essential Techniques and Best Practices
In the world of architecture, engineering, and construction, precision is everything. To bring a design from concept to reality, professionals rely heavily on detailed drawings that outline each structural component with accuracy and clarity. One of the most foundational methods used in this process is Structural 2D Drafting, a technique that has stood the test of time despite advancements in 3D modeling and digital visualization tools. This article delves into the core principles of structural 2D drafting, the essential techniques involved, its applications across industries, and best practices to ensure excellence in every project.
What is Structural 2D Drafting?
Structural 2D drafting is the process of creating two-dimensional representations of structural components, such as beams, columns, walls, and foundations. These drawings are designed to convey all necessary details required for construction, including dimensions, materials, positions, and specific instructions. Unlike 3D modeling, which offers a spatial view of the structure, 2D drafting provides clear and concise outlines focused on accurate measurements and specifications that builders, engineers, and contractors rely on for execution.
Structural 2D drafting is typically created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, which allows drafters to produce precise and scalable drawings. This format provides an accessible and organized way to convey structural information, making it essential for project documentation, compliance with building codes, and coordination among teams.
Key Components of Structural 2D Drafting
A successful structural 2D drawing comprises various components, each serving a distinct purpose. Here are some of the core elements commonly found in structural 2D drafts:
1. Floor Plans
Floor plans are overhead views that show the layout of each level in a building, including the placement of walls, doors, windows, and structural supports. These plans provide a roadmap for construction teams, helping them understand the spatial arrangement and structural distribution within the building.
2. Elevations
Elevations are 2D views of the building’s exterior from different angles. They depict the height and structure of each wall, along with window and door placements, giving a comprehensive view of the building's facade.
3. Sections
Sections are cross-sectional views that show a cut-through of the building’s components, illustrating how floors, walls, and other elements fit together vertically. This component is crucial for understanding load distribution, structural supports, and the overall integrity of the building.
4. Detail Drawings
Detail drawings focus on specific areas or components within the structure, such as joints, connections, or reinforcements. These drawings provide a closer look at intricate parts of the structure, ensuring that each element is constructed according to design standards.
The Importance of Structural 2D Drafting in Modern Construction
While 3D modeling and BIM (Building Information Modeling) have revolutionized the design and construction industries, structural 2D drafting remains a critical component of the drafting process. Here’s why structural 2D drafting is still essential today:
1. Precision and Accuracy
Structural 2D drafting provides a level of precision that is crucial for structural integrity. With detailed measurements and clear instructions, 2D drawings reduce the likelihood of errors during construction, ensuring that each component is built to exact specifications.
2. Compliance with Building Codes
Building codes and regulations are often written with 2D documentation in mind. Structural 2D drawings are easily reviewed by regulatory bodies, simplifying the process of obtaining approvals and ensuring that the structure meets safety standards.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
For projects that do not require complex 3D modeling, structural 2D drafting is a more cost-effective approach. It provides all the necessary information without the additional expense of 3D visualization, making it an ideal choice for small and mid-sized projects.
Best Practices for Effective Structural 2D Drafting
To achieve the highest quality in structural 2D drafting, it’s essential to follow best practices that ensure clarity, precision, and accuracy. Here are some key guidelines:
1. Use Consistent Line Weights and Styles
Different line weights and styles help distinguish between various structural elements, such as load-bearing walls, beams, and columns. Consistency in line weights makes the drawing easier to interpret and reduces the risk of miscommunication.
2. Label Elements Clearly
Every component in the drawing should be labeled clearly to provide unambiguous guidance. Labels for dimensions, materials, and specific instructions are essential for ensuring that builders and engineers understand each aspect of the design.
3. Include Relevant Annotations
Annotations provide additional details about specific components or instructions. Including relevant annotations, such as material specifications or reinforcement details, enhances the drawing’s utility and ensures compliance with design standards.
4. Ensure Accurate Dimensions
Accurate measurements are at the core of structural 2D drafting. Drafters should double-check all dimensions to avoid discrepancies that could lead to structural issues during construction. Using CAD software’s measurement tools can help maintain precision.
Applications of Structural 2D Drafting Across Industries
Structural 2D drafting is used across various sectors, each requiring unique applications. Here are some common applications:
1. Residential Construction
In residential construction, structural 2D drawings outline foundation details, framing layouts, and wall placements. These drawings ensure that homes are built to code and provide homeowners with a clear representation of their property’s structural layout.
2. Commercial Projects
For commercial buildings, 2D drafting helps coordinate complex layouts and structural systems. Detailed floor plans and elevations ensure that these buildings can support high occupancy and meet safety regulations.
3. Industrial Facilities
Industrial projects rely on structural 2D drawings to design frameworks capable of supporting heavy machinery and materials. These drawings are essential for safety in manufacturing plants and warehouses.
4. Infrastructure Projects
Infrastructure projects like bridges and tunnels require highly detailed structural 2D drawings to meet strict safety standards and support the weight of vehicles and materials. Accurate 2D drafts are indispensable in these public projects.
Challenges in Structural 2D Drafting
While structural 2D drafting is a foundational technique, it comes with its own set of challenges:
1. Limited Visualization
Unlike 3D modeling, 2D drawings do not provide a spatial representation, making it harder for stakeholders to visualize complex structures.
2. Misinterpretation Risk
Without proper labeling and annotations, 2D drawings can be misinterpreted. Ensuring clarity and precision in every drawing is essential to avoid costly mistakes.
Structural 2D drafting remains a cornerstone of modern construction and engineering. Its simplicity, precision, and cost-effectiveness make it an invaluable tool for professionals across various sectors. By adhering to best practices and understanding its applications, architects and engineers can continue to rely on structural 2D drafting to bring their visions to life. Whether for residential homes or complex infrastructure, structural 2D drafting ensures that every element of the design is communicated with clarity and accuracy.